논문 제목: scButterfly: a versatile single-cell cross-modality translation method via dual-aligned variational autoencoders
출판 날짜: 2024년 6월
키워드: scButterfly, VAE, cross-modality translation, multi-omics
Abstract
각각의 세포에서 multi-omics를 동시에 profiling하는 최근의 발전은 세포 이질성, 분자 계층 구조 연구를 가능하게 했다. 하지만, 기술적인 한계로 인해 이를 동시에 측정할 경우 비용 문제와, noisy한 데이터가 얻어진다는 한계가 존재한다.
본 논문에서는 dual-aligned variational encoder와 data augmentation 방법을 기반으로 하는 single-cell cross-modality translation 방법, scButterfly를 제안한다.
scButterfly는 다른 방법에 비해 데이터셋을 translating하는 과정에서 세포 이질성을 잘 보존하였고, 세포 유형별 생물학적 인사이트를 밝히는 데 뛰어나다. 또한, single modality 통합 multiomics 분석, 품질이 낮은 단일 세포 multi-omics의 데이터 품질 향상 및 scATAC-seq 데이터의 automatic cell type annotation에 광범위한 적용이 가능하다. scButterfly는 unpaired data training, perturbation-response 분석, consecutive translation으로 generalize될 수 있다.
Introduction
scRNA-seq, scATAC-seq과 같은 single-cell sequencing 기술이 발전했지만, 이들과 같이 단일 모달리티 데이터만 분석하게 되면, 개별 세포 내에서 크로마틴 접근성, 유전자 발현과 같은 요소들이 어떻게 서로 영향을 주고받으며 상호작용하는지에 대해 파악하기 어렵다.
그래서 동시에 여러 모달리티를 profile할 수 있는 기술들이 등장했는데, 이는 lower sensitivity, throughput, higher noise, cost 등의 한계를 가지고 있다.
하지만 단일 모달리티로 존재하는 데이터 양이 매우 많기 때문에, paired multi-omics 상황에서, 정확하게 single-cell cross-modality translation을 하는 것이 더욱 중요해졌다.
기존 방법으로는 BABEL, Polarbear, CLUE, sciPENN 등이 존재하는데, 현재 방법들은 아래와 같은 여러 한계점을 지니고 있다.
- high dimensionality, technical variation
- dropout events
- data augmentation scheme 부족
- batch effects (inter-sample variations 해결X)
- paired multi-modal single-cell profiles이 없을 때의 diagonal strategies 필요
- comprehensive evaluation 부족
따라서 본 논문에서는, scButterfly를 제안하는데, 이는 각 모달리티에 대해 masked VAE를 각각 훈련시켜서 latent factors를 학습하고, 이후 다른 모달리티의 latent represenations를 semantic level에서 dual-align하여 cross-modality 관계를 학습하는 방식이다. Data augmentation scheme도 도입하여 훈련 샘플을 늘리고, unpaired data를 이용한 diagnoal traning을 가능하게 한다.
(주로 scATAC-seq & scRNA-seq 데이터 다룸)
실험 결과, scButterfly는 아래와 같은 장점을 지니는 것으로 확인되었다.
- 기존 baseline methods보다 뛰어난 성능을 보이며 cell heterogeneity를 잘 보존
- 서로 다른 sequencing protocols나 unpaired 또는 sparse한 데이터 환경에서도 안정적인 성능을 유지
- batch effects와 novel cell types를 효과적으로 처리
- integrative multi-omics analysis, poor-quality data enhancement, scATAC-seq data의 자동 cell type annotation을 가능하게 함
- epigenome에서 transcriptome을 거쳐 proteome으로 이어지는 consecutive translations도 성공적으로 수행
Methods
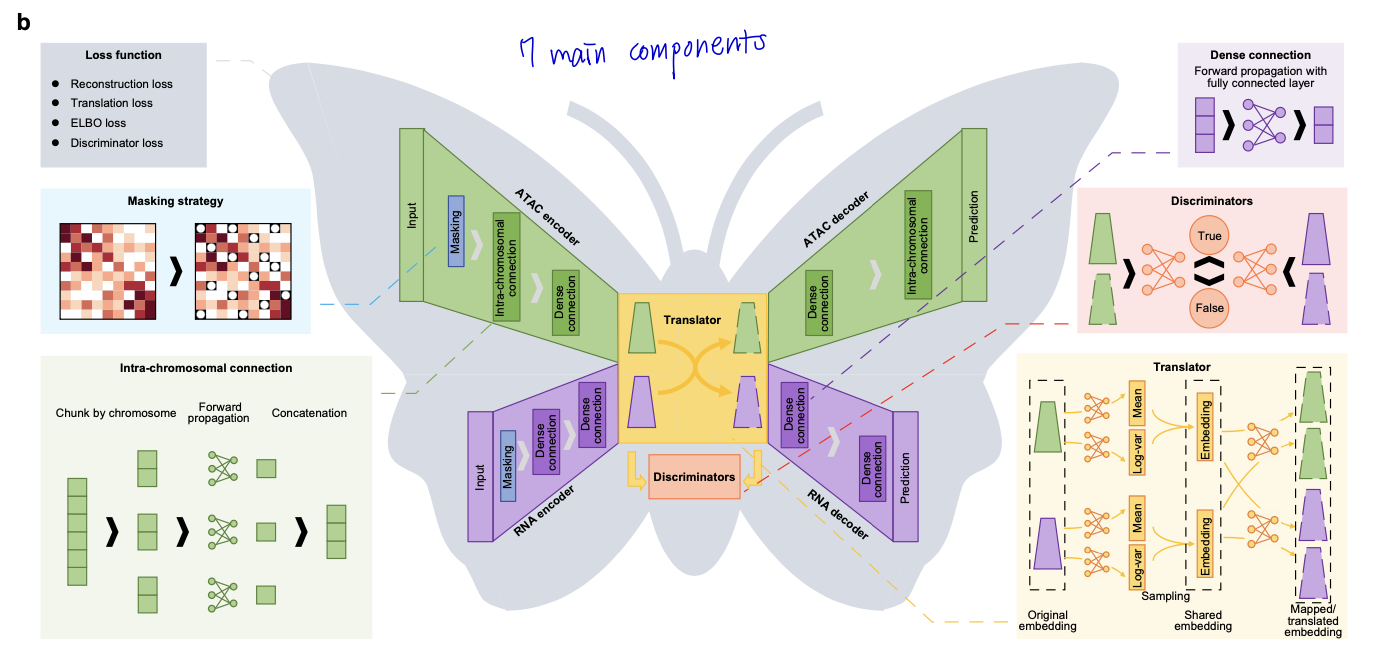
1. 기본 모델 구조
- dual-aligned VAE
- Encoders
- RNA encoder & ATAC encoder : 각각의 오믹스 데이터를 저차원의 latent representations으로 변환
- Masking: 일부 입력 데이터를 랜덤하게 0으로 설정
- ATAC encoder의 경우, intra-chromosomal 연결에 집중하도록 설계함
- Decoders
- RNA decoder & ATAC decoder : latent representations를 다시 원래의 고차원 공간으로 reconstruct
- Translator
- latent space에서 모달리티 간 변환
- 학습된 multivariate Gaussian distributions를 활용하여 변환된 표현 생성
- Discriminators
- 2개의 discriminators
- translator의 입력과 출력이 적절히 정렬되도록 adversarial scheme으로 훈련
⇒ Traning 과정: pretraining → integrative training
- pretraining: 각 모달리티에 대해 VAE를 훈련 (reconstruction loss, ELBO loss 사용)
- integrative training: pretrained된 매개변수를 사용하여 전체 모델을 통합적으로 훈련 (reconstruction loss, translation loss, ELBO loss, discriminator loss 사용)

2. Data Augmentation Strategy
- scButterfly-T (Type): 훈련데이터에 cell-type 라벨이 있는 경우, 동일한 세포 유형에 속하는 두 세포의 RNA profile, ATAC profile을 랜덤하게 짝지어서 synthetic samples 생성
- scButterfly-C (Cluster): 세포 유형 정보가 없는 경우... MultiVI 모델로 세포를 통합 분석하고, Leiden clustering 통해 cluster 라벨을 얻고, 이후 동일 클러스터 내의 세포 profile 짝지어서 synthetic samples 생성
Results
Overview of the scButterfly model
- dual-aligned variational autoencoders
- omics-specific VAE를 통해 인코더, 디코더 파라미터를 pretrain
- 2개 encoders, 2개 decoders, 1개 translator, 2개 discriminators
data augmentation scheme도 제안하였는데, 여기서의 가정은 같은 카테고리 안에 있는 세포들은 비슷한 특징을 가지고 있어서 서로 매치가 가능하다는 것이다. 아래는 각각 cell type annotation이 주어진 상황, 주어지지 않은 일반적인 상황에서 어떻게 데이터 증강을 하는지에 관한 과정을 담고 있는 figure이다.


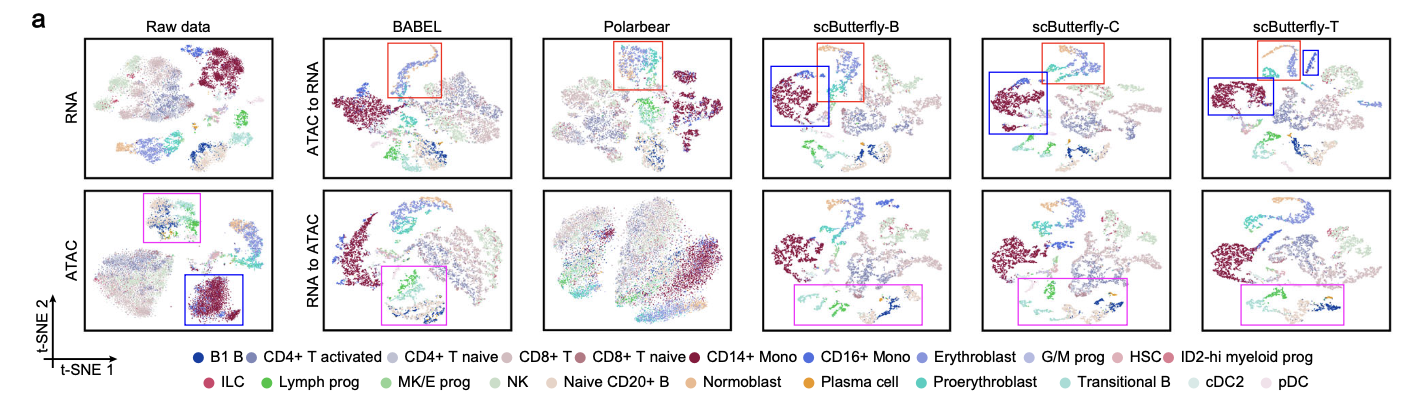
scButterfly enables cross-modality translation while preserving cell heterogeneity
scButterfly는 BMMC 데이터셋을 사용한 cross-validation 실험에서 기존 방법인 BABEL, Polarbear, JAMIE보다 뛰어난 성능을 보였다. 특히, t-SNE 시각화 결과, scButterfly가 예측한 RNA 프로필은 원본 데이터에서 확인하기 어려웠던 세 가지 중요한 세포 유형인 적혈구 생성(erythropoiesis) 단계(proerythroblasts, normoblasts, erythroblasts)를 성공적으로 구분해냈다.
또한, scATAC-seq 데이터에서는 구분하기 어려웠던 CD14+ Mono와 CD16+ Mono 세포 유형도 성공적으로 식별했다.
⇒ 이는 scButterfly가 훈련 데이터의 여러 모달리티에서 얻은 정보를 잘 활용하여 노이즈를 완화하고 세포 유형을 정확히 식별할 수 있음을 보여준다.
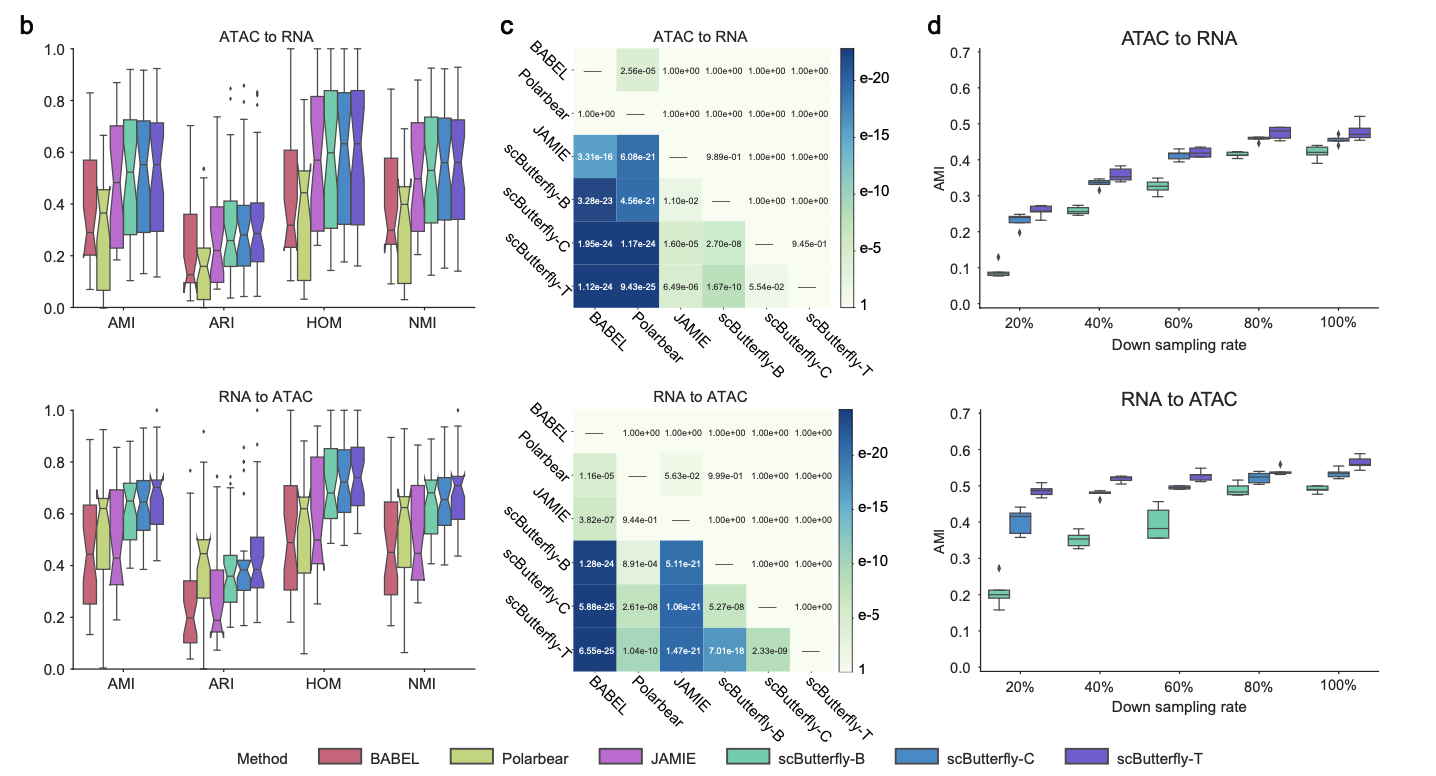
다른 6개의 데이터셋을 포함한 종합적인 평가에서도 scButterfly-B는 기존 방법보다 우수한 성능을 보였다 (Fig. 2b).
특히, Wilcoxon signed-rank test 결과는 scButterfly-B의 장점을 통계적으로 입증했다(Fig. 2c).
또한, scButterfly의 data augmentation schemes을 활용한 scButterfly-C와 scButterfly-T 모델이 기본 모델인 scButterfly-B보다 약간 더 나은 성능을 보였다. 이는 limited sample size 환경에서도 데이터 증강이 변환 성능을 크게 향상시킬 수 있음을 의미한다 (Fig. 2d)
scButterfly effectively translates data of novel contexts and reveals biological insights
이 파트에서는 scButterfly가 훈련 데이터에 없는 새로운 세포 유형이나 inter-sample variations (batch effects)가 포함된 데이터를 얼마나 잘 처리하는지 평가하였다.
- Novel Cell Types: 훈련 데이터셋과 테스트 데이터셋의 세포 유형이 완전히 겹치지 않는 교차 검증 실험에서, 모든 방법의 성능이 전반적으로 감소했음에도 불구하고, scButterfly의 모든 변형 모델이 다른 방법보다 우수한 성능을 보였다 (Fig. 3a). 이는 scButterfly가 단순히 훈련 데이터를 기억하는 것이 아니라 복잡한 세포 간의 관계를 효과적으로 학습한다는 것을 의미한다.
- Batch Effects (배치 효과): 서로 다른 배치(batch)에서 유래한 데이터를 변환하는 실험에서도 scButterfly는 기존 방법보다 더 나은 성능을 보였다 (Fig. 3b) . scButterfly는 noise의 영향을 완화하고, 원본 데이터로는 구분하기 어려웠던 미묘한 세포 유형을 식별하는 것을 확인하였다 (Fig. 3c).
- 생물학적 통찰력 (Biological Insights): scButterfly는 MDS 데이터셋에서 기저 세포(basal cells)를 두 개의 하위 그룹으로 나누고, 이들 하위 그룹이 실제 RNA 데이터에서는 보이지 않던 기능적 통찰(functional insights)을 발견하였다 (Fig. 3d-f). 이는 scButterfly가 단순히 데이터 변환을 넘어 세포 하위 유형(subtypes)을 식별하고, 특정 생물학적 과정과 관련된 differentially expressed genes (DEGs)를 찾아내는 데 도움을 줄 수 있음을 보여준다.

scButterfly facilitates integrative analysis, data enhancement, and cell type annotation
- 통합 분석(Integrative Analysis): 단일 모달리티 데이터만 있는 경우, scButterfly가 예측한 다른 모달리티 프로필을 통합하면 원본 multi-omics data를 통합한 것과 유사하거나 더 나은 성능으로 세포 이질성을 분석할 수 있다 (Fig. 4a, b).
- 데이터 개선(Data Enhancement): 노이즈가 심한 데이터셋(MK, MB)에 대해 scButterfly로 예측된 데이터를 사용하면 원본 데이터보다 세포 하위 그룹을 더 잘 특성화하고 클러스터링 성능을 향상시킬 수 있다 (Fig. 4c).
- 세포 유형 주석(Cell Type Annotation): scATAC-seq 데이터에 대한 자동 세포 유형 주석에서 scButterfly-C와 SVM, 또는 Cellcano 분류기를 조합한 모델이 기존의 EpiAnno 및 Cellcano 방법보다 높은 정확도를 보였다 (Fig. 4d, e).

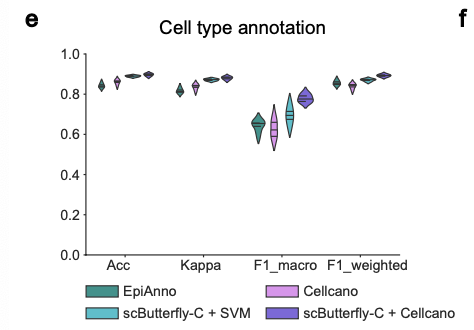
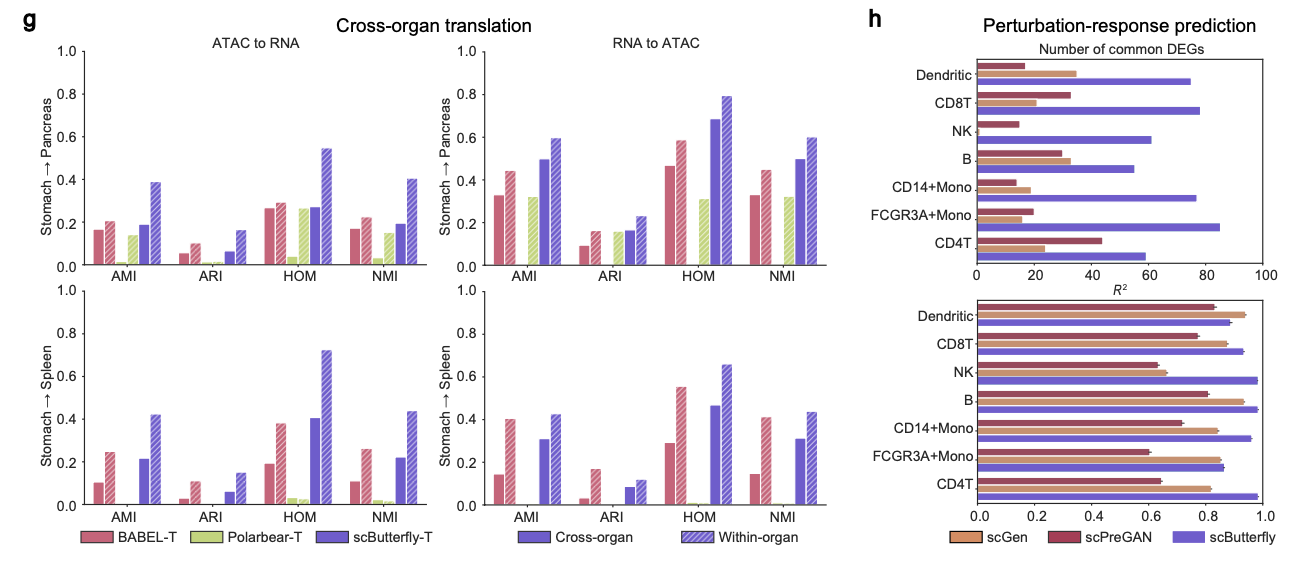
scButterfly can be generalized to unpaired data training and perturbational analysis
- Unpaired Data Training: unpaired single-cell data를 사용한 실험에서도 scButterfly는 다른 방법들보다 월등히 높은 세포 집단 식별 정확도를 보였다 (Fig. 4f).
- Cross-organ translation: 서로 다른 장기(organ)의 데이터를 변환하는 더 어려운 작업에서도 scButterfly는 기존 방법들보다 일관되게 우수한 성능을 보였다 (Fig. 4g).
- Perturbation-response prediction: scButterfly는 single-cell perturbation-response prediction 작업에서도 최신 방법인 scGen과 scPreGAN보다 훨씬 뛰어난 성능을 보였다 (Fig. 4h)

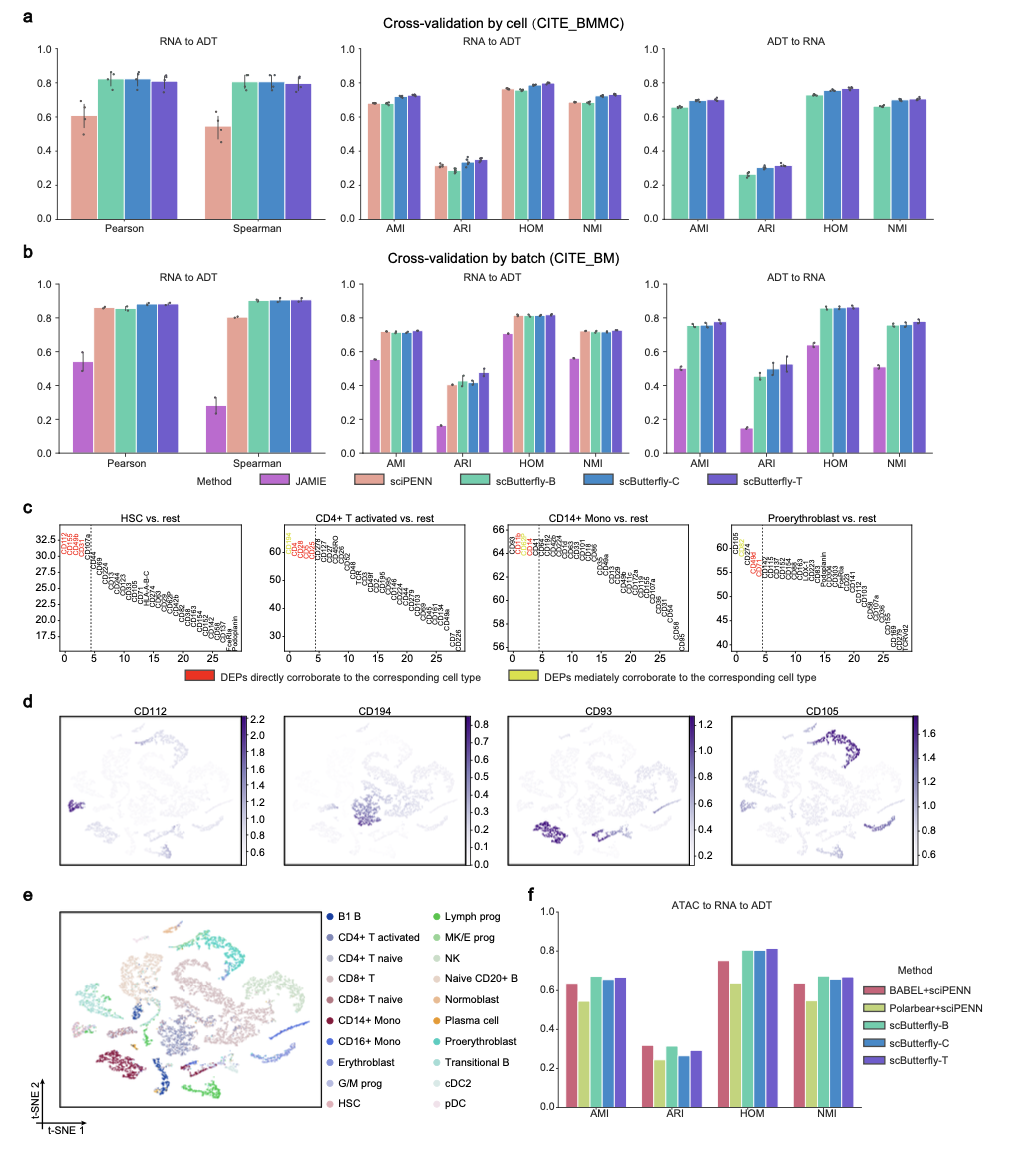
scButterfly enables consecutive translation from epigenome to transcriptome to proteome
이 부분에서는 epigenome, transcriptome, proteome 세 가지 모달리티를 연속적으로 변환하는 가능성을 보여준다.
- Transcriptome-Proteome 변환: CITE-seq 데이터셋을 사용한 실험에서 scButterfly는 sciPENN 및 JAMIE와 비교하여 같거나 더 나은 성능을 보였다 (Fig. 5a, b).
- 연속적 변환(Consecutive Translation): scATAC-seq 데이터에서 RNA를 거쳐 ADT(Proteome)까지 변환하는 실험에서, 예측된 ADT 프로필은 세포 유형별 특성을 잘 보존했고, 기존 연구와 일치하는 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs)를 찾아냈다 (Fig. 5c-e). 이는 scButterfly가 직접 프로파일링하기 어려운 두 모달리티 간의 변환을 가능하게 하며, 중요한 생물학적 의미를 제공한다는 것을 보여준다.
Discussion
scButterfly는 dual-aligned VAEs와 data augmentation schemes를 기반으로 하는 다재다능한 single-cell cross-modality translation 방법이다. 다양한 데이터셋에 대한 실험을 통해 scButterfly의 우수한 성능이 입증되었으며, 세포 이질성 보존, novel cell types나 batch effects가 있는 데이터 변환, 그리고 integrative multi-omics analysis, data enhancement, cell type annotation 등 광범위한 응용 분야에서 그 장점이 확인되었다.
또한, 본 논문은 scButterfly의 추가 개선 방향을 제안한다.
- 공개된 데이터 및 사전 지식 통합: 공공 bulk omics data나 cell atlas를 활용하여 cell heterogeneity 특성화를 강화하거나, gene regulatory mechanisms에 대한 사전 지식을 통합하여 다른 모달리티 간의 연결을 더욱 공고히 할 수 있다.
- 모달리티 확장: spatial transcriptomics나 single-cell Hi-C data와 같은 새로운 모달리티를 유연하게 수용하도록 프레임워크를 확장할 수 있다.
- 고급 머신러닝 기법 적용: adaptive하고 interpretable한 모델 매개변수를 가진 고급 machine learning techniques를 적용하여 cross-cell-type 및 cross-organ translation 성능을 더욱 향상시킬 수 있다.
